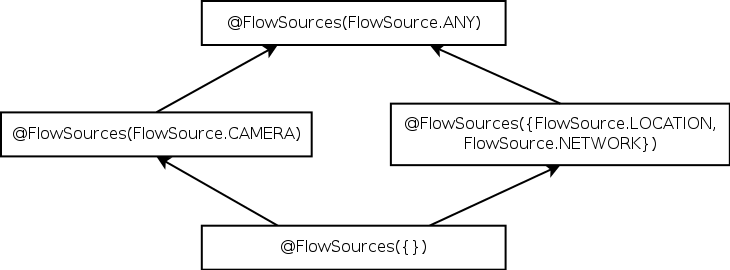
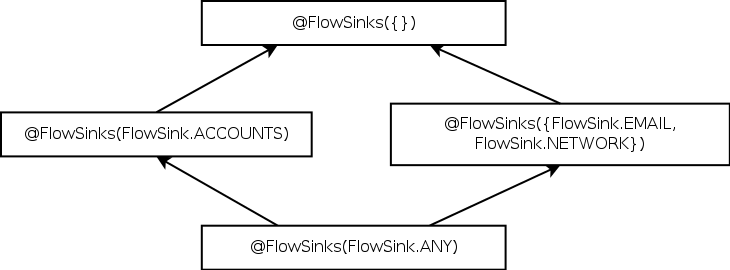
| Figure 3.1: Partial qualifier hierarchy for flow source and flow sink type qualifiers, expressed as Java annotations @Source and @Sink. |
SPARTA! |
SPARTA is a research project at the University of Washington funded by the DARPA Automated Program Analysis for Cybersecurity (APAC) program.
SPARTA aims to detect certain types of malware in Android applications, or to verify that the app contains no such malware. SPARTA’s verification approach is type-checking: the developer states a security property, annotates the source code with type qualifiers that express that security property, then runs a pluggable type-checker [PAC+08, DDE+11] to verify the type qualifiers (and thus to verify that the program satisfies the security property).
You can find the latest version of this manual in the sparta-code version control repository, in directory sparta-code/docs. Alternately, you can find it in a SPARTA release at https://types.cs.washington.edu/sparta/release/, though that may not be as up-to-date.
The SPARTA toolset contains two types of tools: reverse engineering tools to find potentially dangerous code in an Android app, and a tool to statically verify information flow properties.
The reverse engineering tools to find potentially dangerous code can be run on arbitrary unannotated Android source code. Those tools give no guarantees, however; they just direct the analyst’s attention to suspicious locations in the source code.
By contrast, the tools to statically verify information flow require a person to write the information flow properties of the program, primarily as source code annotations. For instance, an object that contains data that came from the camera and is destined for the network would be annotated with
@Source(CAMERA) @Sink(INTERNET)
There are two different scenarios in which the SPARTA tools might be used.
In this case, the analyst merely re-runs the static information flow tool to confirm the vendor’s work. This shows that there are no undesired information flows in the program.
Chapter 4 explains how to use the SPARTA tools for this scenario.
In this case, it is most efficient to first run the reverse engineering tools to detect suspicious code. Those tools might reveal unacceptable code: either malware or code that the vendor should rewrite in a clearer or safer way. If the suspicious code detection tools do not reveal problems so severe that the app should be rejected, then they help to guide the next step. The analyst writes information flow annotations and runs the information flow tool until either the analyst has found a vulnerability or the lack of tool warnings indicates there is no vulnerability.
Chapter 5 explains how to use the SPARTA tools for this scenario.
If you have trouble, please email either sparta@cs.washington.edu (developers mailing list) or sparta-users@cs.washington.edu (users mailing list) and we will try to help.
This chapter describes how to install the SPARTA tools (Section 2.2) and how to prepare an Android App to have the SPARTA tools run on it (Section 2.3).
If using Eclipse, go to Help → Install New Software and install the Android ADT Plugin (https://dl-ssl.google.com/android/eclipse).
hg clone https://dada.cs.washington.edu/hgweb/sparta-codeusing the credentials you have been given.
Then, unpack the archive.
ant jar
ant all-tests
You should see “BUILD SUCCESSFUL” at the end.
This section explains how to set up an Android application for analysis with the SPARTA tools.
$ANDROID_HOME/tools/android update project --path .
</project>. <property name="checkers" value="${env.CHECKERS}"/>
<property name="sparta-code" value="${env.SPARTA_CODE}"/>
<dirname property="checkers_dir" file="${checkers}" />
<basename property="checkers_base" file="${checkers}" />
<dirname property="sparta-code_dir" file="${sparta-code}" />
<basename property="sparta-code_base" file="${sparta-code}" />
<import file="${sparta-code_dir}/${sparta-code_base}/build.include.xml" />
To use Eclipse to look at and build the code, perform these simple steps:
Most Android apps will rely on an auto-generated R.java file in the /gen directory of the project. This will only be generated if there are no errors in the project. There may be errors in the resources (.../res directory) that could cause R.java to not be generated.
Additionally, if the app depends on an external .jar file (often located in the lib/ directory), it will compile in Eclipse but not with Ant. To fix this, in ant.properties, add “jar.libs.dir=lib” (or wherever the .jar is located).
This chapter describes the Flow Checker, a type-checker that tracks information flow through your program. The Flow Checker does pluggable type-checking of an information flow type system. It is implemented using the Checker Framework. This chapter is logically a chapter of the Checker Framework Manual (http://types.cs.washington.edu/checker-framework/current/checkers-manual.html). Therefore, in order to understand this chapter, you should first read chapters 1–2 of the Checker Framework Manual, and you should at least skim chapters 18–21 (generics through libraries) and 24–25 (FAQ and troubleshooting).
To use the Flow Checker, a programmer must supply two types of information:
When you run the Flow Checker, it verifies that the annotations in the program are consistent with what the program’s code does, and that the annotations are consistent with the flow policy. This gives a guarantee that the program has no information flow beyond what is expressed in the flow policy and type annotations.
After you read this chapter, see Chapter 6 for tips about writing information-flow annotations.
The type qualifier @Source on a variable’s type indicates what sensitive sources might affect the variable’s value. The type qualifier @Sink indicates where (information computed from) the value might be output. These qualifiers can be used on any occurrence of a type, including in type parameters, object instantiation, and cast types.
As an example, consider the declaration
@Source(LOCATION) @Sink(INTERNET) double loc;
The type of variable loc is @Source(LOCATION) @Sink(INTERNET) double. The @Source(LOCATION) qualifier indicates that the value of loc might have been derived from location information. Similarly, the qualifier @Sink(INTERNET) indicates that loc might be output to the network. A programmer typically writes either @Source or @Sink, but not both; see Section 3.3. It is also possible that the data has already been output.
The arguments to @Source and @Sink are permissions drawn from our enriched permission system (Section 3.1.2). The argument may also be a set of permissions to indicate that a value might combine information from multiple sources or flow to multiple locations. The rarely-used special constant ANY denotes the set of all sources or the set of all sinks.
Figure 3.1: Partial qualifier hierarchy for flow source and flow sink type qualifiers, expressed as Java annotations @Source and @Sink.
A type qualifier hierarchy indicates which assignments, method calls, and overridings are legal, according to standard object-oriented typing rules. Figure 3.1 shows parts of the @Source and @Sink qualifier hierarchies.
@Source(B) is a subtype of @Source(A) iff B is a subset of A. For example, @Source(INTERNET) is a subtype of @Source({INTERNET, LOCATION}). This rule reflects the fact that the @Source annotation places an upper bound on the set of sensitive sources that were actually used to compute the value. If the type of x contains @Source({INTERNET, LOCATION}), then the value in x might have been derived from both INTERNET and LOCATION data, or only from INTERNET, or only from LOCATION, or from no sensitive source at all.
The opposite rule applies for sinks: @Sink(B) is a subtype of @Sink(A) iff A is a subset of B. The type @Sink({INTERNET, LOCATION}) indicates that the value is permitted to flow to both INTERNET and FILESYSTEM. This is a subtype of @Sink(INTERNET), as the latter type provides fewer routes through which the information may be leaked.
The Flow Checker is finer-grained than standard Android manifest permissions in two ways. First, Android permits any flow between any pair of permissions in the manifest — that is, any resource mentioned in the manifest may be used in an arbitrary way. Second, the Flow Checker uses finer-grained permissions than Android does, in particular by adding additional permissions. Such finer-grained analysis is necessary in order to detect Trojans that would look innocuous, given Android’s coarser model. For example, the Flow Checker requires a permission to retrieve data from the accelerometer, which can indicate the user’s physical activity, and to retrieve the time of day, which can be used as a trigger for malicious behavior.
Our system does not add much complexity: it only adds 28 permissions to Android’s standard 130, or 22% more permissions. Table 3.1 lists the additional permissions.
Table 3.1: Additional permissions used by the Flow Checker, beyond the built-in 130 Android permissions.
Sources Sinks Both source and sink ACCELEROMETER CONDITIONAL CAMERA_SETTINGS BUNDLE DISPLAY CONTENT_PROVIDER LITERAL SPEAKER DATABASE MEDIA WRITE_CLIPBOARD FILESYSTEM PHONE_NUMBER WRITE_EMAIL INTENT RANDOM WRITE_LOGS PARCEL READ_CLIPBOARD PROCESS_BUILDER READ_EMAIL SECURE_HASH READ_TIME SHARED_PREFERENCES REFLECTION SQLITE_DATABASE USER_INPUT SYSTEM_PROPERTIES
We now discuss two permissions, LITERAL and CONDITIONAL, and empty whose meaning may not be obvious.
The LITERAL source is used for programmer-written manifest constants, such as "Hello world!". This enables the Flow Checker to distinguish information derived from the program source code from other inputs. Manifest literals are used benignly for many purposes, such as configuring default settings. The flow policy shows the ways they are used in the program, and they can be directly examined by the analyst.
The Flow Checker treats conditional statements as a flow sink to enable detection of indirect flows that leak private information. For example, without any treatment of conditionals, the following code would be permitted under a flow policy containing LITERAL→INTERNET and USER_INPUT→FILESYSTEM:
@Source(USER_INPUT) @Sink(FILESYSTEM)
long creditCard = getCCNumber();
final long MAX_CC_NUM = 9999999999999999;
for (long i = 0 ; i < MAX_CC_NUM ; i++) {
if (i == creditCard)
sendToInternet(i);
}
To prevent malicious developers from bypassing the type system in this manner, the Flow Checker requires the type of a conditional expression to include the sink CONDITIONAL. By default, literals are allowed to flow to a conditional; that is, LITERAL→CONDITIONAL is added to the flow policy by default.
Data containing sensitive information is often passed through conditional statements for benign reasons. For example, an app might verify that a credit card number entered is valid by checking the number of digits.
@Source(USER_INPUT) @Sink(FILESYSTEM)
long creditCard = getCCNumber();
final long MAX_CC_NUM = 9999999999999999;
if (MAX_CC_NUM < creditCard)
reportTooManyDigits();
In this case, the credit card number is not indirectly leaked, but the Flow Checker cannot determine this and will report a false positive. The auditor must examine the code nearby to ensure that the conditional is not being used to indirectly leak information.
Programmers should not use @Source({}) or @Sink({}) for any types except in stub files. These types are only needed for top/bottom types which are used in the default types: the null literal uses the bottom type in order for it to be assignable everywhere; local variables use the top type which will be refined by flow sensitivity. Every value should either flow from a literal or from some sensitive source. Likewise, every value must flow to a sensitive sink or to a conditional expression. Any variable that does not have a flow source or a flow sink does not actually affect the output of the program and should therefore be removed.
This may seem overly strict, but a variable without a flow source or flow sink that does affect the output of the program comes from an abuse of the type system. Most likely a variable with no source or sink would come from an improperly suppressed warning. Therefore it is necessary to not allow flows from and to nowhere. (The flow policy ensures this; see section Section 3.2.
Note that this does not mean you must specify both a flow source annotation and a flow sink annotation as explained in Section 3.3.
A flow policy is a list of all the flows that are permitted to occur in an application. A flow policy file expresses a flow policy, as a list of flowsource*→flowsink* pairs. Just as the Android manifest lists all the permissions that an app uses, the flow policy file lists the flows among permissions and other sensitive locations.
The Flow Checker guarantees that there is no information flow except for what is explicitly permitted by the policy file. If a user writes a type that is not permitted by the policy file, then the flow checker issues a warning even if all types in program otherwise typecheck.
For example, this variable declaration
@Source(CAMERA) @Sink(INTERNET) Video video = ...
is illegal unless the the policy file contains:
CAMERA -> INTERNET
Here is another example. The flow policy file contains:
ACCOUNTS -> EXTERNAL_STORAGE, FILESYSTEM ACCELEROMETER -> EXTERNAL_STORAGE, FILESYSTEM, INTERNET
The following variable declarations are permitted:
@Source(ACCOUNTS) @Sink(EXTERNAL_STORAGE) Account acc = ... @Source(ACCELEROMETER, ACCOUNTS) @Sink(EXTERNAL_STORAGE, FILE_SYSTEM) int accel = ...
The following definitions would generate “forbidden flow” errors:
@Source(ACCOUNTS) @Sink(@INTERNET) Account acc = ...
@Source({ACCELEROMETER, ACCOUNTS})
@Sink({EXTERNAL_STORAGE, FILESYSTEM, INTERNET})
The flow policy file indicates specific permitted information flows. It may be possible to combine these flows. For example, a policy that permits CAMERA→FILESYSTEM and FILESYSTEM→INTERNET will implicitly allow the flow CAMERA→INTERNET, because the application may record from the camera into a file and then send the contents of the file over the network. The Flow Checker forbids such implied flows: the developer is required to write the transitive flow in the flow policy file, which requires the developer to justify its purpose or convince the app store that the flow is not used. Finer-grained permissions, as discussed in
Each line of a policy file specifies a permitted flow from a source to one or more sinks. For example, MICROPHONE -> INTERNET implies that MICROPHONE data is always allowed to flow to INTERNET. The source or sink must be a member of the enum sparta.checkers.quals.FlowPermission. The source and sink names should not be preceded by the name of the enumeration which contains them. ANY is allowed just as it is in @Source and @Sink, but empty, {}, is not allowed.
Multiple sinks can appear on the same line if they are separated by commas. For example, this policy file:
MICROPHONE -> INTERNET, LOG, DISPLAY
is equivalent to this policy file:
MICROPHONE -> INTERNET MICROPHONE -> LOG MICROPHONE -> DISPLAY, INTERNET
The policy file may contain blank lines and comments that begin with a number sign (#) character.
To use a flow-policy file when invoking the Flow Checker from the command line pass it the option:
-AflowPolicy=mypolicyfile
Or if you are using the check-flow ant targets, you can pass the option to ant:
ant -DflowPolicy=mypolicyfile check-flow
A complete type consists of a @Source qualifier, a @Sink qualifier, and a Java type. To reduce programmer effort and code clutter, most of the qualifiers are inferred or defaulted.
A programmer need not write qualifiers within method bodies, because such types are inferred by the Flow Checker (see Section 3.3.1). Even for method signatures and fields, a programmer generally writes either @Source or @Sink, but not both; see Section 3.3.2 and Section 3.3.3.
A programmer does not write information flow types within method bodies. Rather, local variable types are inferred.
The Flow Checker implements this inference via flow-sensitive type refinement. Each local variable declaration defaults to the top type, @Source(ANY) Source({}). At every properly-typed assignment statement, the type of the left-hand side expression is flow-sensitively refined to that of the right-hand side, which must be a subtype of the left-hand side’s declared type. The refined type applies until the next side effect that might invalidate it. For details, see section “Automatic type refinement (flow-sensitive type qualifier inference)” in the Checker Framework Manual.
We limit type inference to local variables to ensure that each method can be type-checked in isolation, with a guarantee that the entire program is type-safe if each method has been type-checked. It would be possible to perform a whole-program type inference, but such an approach would not be modular, would be heavier-weight, would not deal well with cooperating or communicating applications, and would provide fewer documentation benefits.
If a type contains only a flow source or only a flow sink, the other qualifier is filled in with the most general one that is consistent with the policy file. If the programmer writes @Source(α), the Flow Checker defaults this to @Source(α) @Sink(ω) where ω is the set of flow sinks that all sources in α can flow to. Similarly, @Sink(ω) is defaulted to @Source(α) @Sink(ω) where α is the set of flow sources allowed to flow to all sinks in ω. Defaults are not applied if the programmer writes both a source and a sink qualifier.
For example, suppose the flow policy contains the following:
A -> X,Y
B -> Y
C -> Y
Then these pairs are equivalent:
|
This mechanism is useful because oftentimes a programmer thinks about a computation in terms of only its sources or only its sinks. The programmer should not have to consider the rest of the program that provides context indicating the other end of the flow.
This defaulting mechanism is essential for annotating libraries. The Flow Checker ships with manual annotations for more than 10,000 methods of the Android standard library. 92% of methods use only a @Source or @Sink annotation but not both. An example is the File constructor: a newly-created readable file should be annotated with @Source(FILESYSTEM), but there is no possible @Sink annotation that would be correct for all programs. Instead, the @Sink annotation is omitted, and our defaulting mechanism provides the correct value based on the application’s flow policy.
This mechanism can be viewed as another application of type polymorphism.
Table 3.2: Default information-flow qualifiers for unannotated types
Location Default Flow Type @Source(α) @Source(α) @Sink(ω), ω is the set of sinks allowed to flow from all sources in α @Sink(ω) @Source(α) @Sink(ω), α is the set of sources allowed to flow to all sinks in ω Method parameters @Sink(CONDITIONAL) Method receivers @Sink(CONDITIONAL) Return types @Source(LITERAL) Fields @Source(LITERAL) null @Source({}) @Sink(ANY) Other literals @Source(LITERAL) Type arguments @Source(LITERAL) Local variables @Source(ANY) @Sink({}) Upper bounds @Source(ANY) @Sink({}) Resource variables @Source(ANY) @Sink({})
Table 3.2 shows defaults for completely unannotated types. The Flow Checker allows a developer to choose a different default for a particular method, class, or package. When the default is only a source or only a sink, the other qualifier is inferred from the policy file as explained in Section 3.3.2.
Most unannotated types (including field types, return types, generic type arguments, and non-null literals) are given the qualifier @Source(LITERAL). This is so that simple computation involving manifest literals, but not depending on Android permissions, does not require annotations.
As is standard, the null literal is given the bottom type qualifier, which allows it to be assigned to any variable. For the Flow Checker, the bottom type qualifier is Source({})@Sink(ANY).
There is a difference between a library method being given no @Source annotation and no @Sink annotation (in which case it is defaulted exactly as above) and a library method that has not yet been examined by a human to write a summary. Unexamined methods are conservatively given a special type that guarantees a type-checking error, thus signaling to the developer the need to annotate that library method.
Sometimes it might be necessary to suppress warnings or errors produced by the Flow Checker. This can be done by using the @SuppressWarnings("flow") annotation on a variable, method, or (rarely) class declaration. Because this annotation can be used to subvert the Flow Checker, its use is considered suspicious. Anytime a warning or error is suppressed, you must write a brief comment justifying the suppression. @SuppressWarnings("flow") should only be used if there is no way to annotate the code so that an error or warning does not occur. Most programs should not suppress warnings.
Annotations for API methods are found in the stub files in sparta-code/src/sparta/checkers/flowstubfiles. For details, see section 5.3.1 of this manual, and also chapter “Annotating Libraries” in the Checker Framework Manual. The methods that are annotated in stub files are defaulted the same way as methods written in apps, including flow policy inference. (See the defaulting section, Section 3.3.)
Any method not written in the stub files or found in source code is not defaulted normally. Instead, their return, receiver, and parameter types are annotated with @Sources(NOT_REVIEWED) @Sinks(NOT_REVIEWED). The FlowPermission NOT_REVIEWED is not allowed in a policy file and in no subtype relation. This way, if such an API method is used, a type error will occur and alert the user to review and annotate the method. Althought it is possible to ignore these kind of warnings as explained in section Section 5.3.3. The Flow Checker also outputs all of the methods missing from the stub files in a file called missingAPI.astub in the current working directory. It also contains a comment the number of times an API method is used by the app.
Information flow type qualifiers interact seamlessly with parametric polymorphism (Java generics). For example, a programmer can declare
List<@Source(CONTACTS) @Sink(SMS) String> myList;
Here, the elements of myList are strings that are obtained from CONTACTS and that may flow to SMS.
The Flow Checker also supports qualifier polymorphism, in which the type qualifiers can change independently of the underlying type. This allows a programmer to write a generic method that can operate on values of any information flow type. For example, if a method is declared as @PolySource int f(@PolySource int x), then it can be called on an int with any flow sources, and the result has exactly the same sources as the input. This can be viewed as a declaration and two uses of a type qualifier variable. The implicit type qualifier variables are automatically instantiated by the Flow Checker at the point of use.
For brevity, the additional annotation @PolyFlow can be written on a class or method declaration to indicate that all contained parameters and return types should be annotated as @PolySource @PolySink. @PolyFlow does not override explicitly-written annotations.
Parametric polymorphism, qualifier polymorphism, and regular Java types can be used together. The type system combines the qualifier variables and the Java types into a complete qualified type.
See section “Qualifier polymorphism” in the Checker Framework Manual.
The Flow Checker has additional declaration annotations that are shorthand for common annotation patterns on method signatures. They override the usual defaulting of method declarations.
Annotation @PolyFlow expresses that each contained method should be annotated as @PolySource @PolySink for both the return types and all parameters. It should be used to express a relationship between the parameters and the return types.
Annotation @PolyFlowReceiver expresses that each contained method should be annotated as @PolySource @PolySink for the return type, all parameters types and the receiver type.
If @PolyFlow or @PolyFlowReceiver is written on a class or package, then the annotation applies to all contained methods or classes unless those classes or methods are annotated with another declaration annotation.
This change of defaulting happens to library methods that are not written in stub files. For example, the class Integer as been annotated with @PolyFlowReceiver, but the toString method is not listed in the stub file. This method is inferred to be annotated with @PolyFlowReceiver and therefore its use will not result in a type error involving the NOT_REVIEWED FlowPermission.
By default, the flow checker is unsound. After getting the basic checks to pass, the stricter checks should be enabled, by running ant -Dsound=true check-flow. This two-phase approach was chosen to reduce the annotation effortand to give two separate phases of the annotation effort. The sound checking enforces invariant array subtyping and type safety in downcasts.
When strict checks are turned on, a cast (Object []) x, were x is of type Object, will result in a compiler warning:
[jsr308.javac] ... warning: "@Sink @Source(ANY) Object"
may not be casted to the type "@Sink @Source Object"
The reason is that there is not way for the type-checker to verify the component type of the array. There is no static knowledge about the actual runtime values in the array and important flow could be hidden. The analyst should argue why the downcast is safe.
Note that the main qualifier of a cast is automatically flow-refined by the cast expression.
Stricter checking also enforces invariant array subtyping, which is needed for sound array behavior in the absence of runtime checks. Flow inference automatically refines the type of array creation expressions depending on the left-hand side.
Enabling stricter checking will also enable the -Alint=strict-conditional option to limit allowed sinks to conditionals.
If you are presented with an annotated app, you can confirm the work of the person who did the annotation by answering affirmatively three questions.
Run the Flow Checker (Chapter 3) to ensure that there is no data flow in the application beyond what is expressed in the given flow policy:
ant -DflowPolicy=myflowpolicy check-flow
If the Flow Checker produces any errors or warnings, then the app has not been properly annotated and should be rejected.
Does the flow-policy file match the application description? There should not be any flows that are not explained in the description. These flows may be explicitly stated, such as “encrypt and sign messages, send them via your preferred email app.” Or a flow may only be implied, such as “This Application allows the user to share pics with their contacts.” In the first example, you would expect an EMAIL sink to appear somewhere in the policy file. In the second, “share” could mean a you would see a Flow Sink of EMAIL, SMS, INTERNET, or something else. Flows that are only implied in the description could be grounds for rejection if the description is too vague.
Does the justification for every @SuppressWarnings make sense? Search for every instance of @SuppressWarnings("flow") and read the justification comment. Compare the justification to the actual code and determine if it make sense and should be allowed. No justification comment could be grounds for rejection.
If you are presented with an unannotated app and wish to confirm that it contains no malware, then you need to perform three tasks:
More specifically, the recommended workflow is:
Write a flow-policy file. Section 3.2 describes flow policies.
Read the App description and user documentation, looking for clues about the permissions, sensitive sources, and sinks and how information flows between them. For example, if this is a map app, does the description say anything about sending your location data over the network? If so, then you should add LOCATION→INTERNET to the flow-policy file. Where else does the description say location data can go?
Theoretically, you should be able to write a complete Flow Policy from the description if the description is well-written and the app does not contain malware. In practice, you will have to add flows to the policy file as you more fully annotate the app, but you should ensure that they are reasonable and make note of what additional flows you had to add.
Look at the AndroidManifest.xml file and:
(If you are short on time, you could start with reading the manifest file rather than first reading the app description as recommended in Section 5.1.1. But determining the permissions from the documentation will be more effective in finding problems in either the documentation or the code.)
Run
ant reportsuspicious
to get a list of the most suspicious code locations. The code may be innocuous, but a human should examine it.
This target reports
The file sparta-code/src/sparta/checkers/suspicious.astub contains the classes and methods that are considered suspicious.
The following example from the suspicious.astub file reports all calls
of the invoke method and, additionally, all constructor calls
of the class java.util.Random:
package java.lang.reflect;
class Method {
@ReportCall
public Object invoke(Object obj, Object [] objs) {}
}
package java.util;
@ReportCreation
class Random {}
.java and strings.xml files. The searched-for patterns
appear in the script sparta-code/suspicious.pl.If you learn of additional suspicious API uses or String patterns, please inform the SPARTA developers so they can add them to the suspicious.astub or suspicious.pl file.
Run
ant check-permissions
to see where the application calls API methods that may require some Android permissions. The ant check-permissions tool will help you gain an understanding of how your app first obtains information from a sensitive source, or how your app finally sends information to a sensitive sink. This may help you decide what parts of the app to further investigate, or where to start your annotation work.
There are three possible types of errors you will see. The first error:
MainActivity.java:35:
error: Call require permission(s) [android.permission.SET_WALLPAPER],
but caller only provides []!
clearWallpaper();
^
This error means the method requires one or more permissions which the caller does not have. The second error:
MediaPlayerActivity.java:218:
error: Call may additionally require permission(s)
[android.Manifest.permission.WAKE_LOCK], but caller only provides []!
Notes: WAKE_LOCK is required if MediaPlayer.setWakeMode has been called first.
stop();
^
This error means the method may or may not require one or more permissions which the caller does not have. An explanation for the current error can be seen on the Notes.
HelloWorldActivity.java:83: warning: If the constant DeviceAdminReceiver.ACTION_DEVICE_ADMIN_ENABLED
is passed to an intent it will require following permission(s): [android.permission.BIND_DEVICE_ADMIN]!
i.setAction(DeviceAdminReceiver.ACTION_DEVICE_ADMIN_ENABLED);
^
This error means that the constant used depends on one or more permissions.
You can eliminate the first 2 errors by writing @RequiredPermissions(android.Manifest.permission.PERMISSION) or @MayRequiredPermissions(android.Manifest.permission.WAKE_LOCK) in front of the method header in the source code, if you would like to propagate the required permission up the call stack. You should use @MayRequiredPermissions( value=android.Manifest.permission.PERMISSION, notes=java.lang.String) in case the permission may be required and you should explain the reason on the notes argument. However, it is not necessary to eliminate all the errors from RequiredPermissions. The check-permissions tool is only a tool to guide your annotation and manual analysis effort.
Any permission that is required should already be listed in the AndroidManifest.xml file.
The permissions required by the Android API appear in file src/sparta/checkers/permission.astub, expressed as @RequiredPermissions and @MayRequiredPermissions annotations.
When the goal is to completely annotate an application it is most effective to write information flow annotations in a bottom up approach: first annotate libraries your code uses, then your packages and classes that use those libraries, and so forth up to the entry points of your application. Alternatively, when the goal is to investigate specific information flows, it is more effective to trace and annotate only the flows of interest. Libraries should still be annotated first for all flows types. A bottom up approach can be used as a first pass to annotate large portions of an application while tracing can be then used to find and fix remaining Flow Checker warnings. Both approaches use the flow-policy create in Section 5.1.
Section 5.3.1 describes how to annotate libraries, Section 5.3.2 and Section 5.3.3 describe how to annotate your own code in a bottom up approach, and Section 5.3.4 describes how to iteratively trace sensitive sources in your application.
When the Flow Checker type-checks your code that calls a library API, the Flow Checker needs to know the effect of that call. Stub files in sparta-code/src/sparta/checkers/flowstubfiles/ provide that information. You may need to enhance those stub files, if they do not yet contain information about the library APIs that your application uses. (Over time, the stub files will become more complete, and you will have to do less work in this step for each new app.)
Run ant check-flow to create the missingAPI.astub file. For each method in the file do the following.
If the method does is not directly related to information flow (its inputs and outputs could be anything and are not required to have a specific @Source annotation), then either added the method to the stub file with no annotations, which is the same as annotating the returns and parameters with @Source(LITERAL) or to annotate it with @PolyFlow or @PolyFlowReceiver, which essentially says that the output can have all the flow sources and sinks of the inputs.. (See Section Section 3.7 for more details.)
Important: After changing or adding stub files, run ant jar to rebuild sparta.jar.
The stub files can include any third-party library that is not compiled along with your application. You can add a new .astub file to the flowstubfiles/ directory. Alternately, you can put a new .astub file elsewhere and then pass this file to the ant check-flow target:
ant -Dstubs=path/myAnnoLib.astub check-flow
Here is an example from a stub file:
package android.telephony;
class TelephonyManager {
public @Source(FlowPermission.PHONE_NUMBER) String getLine1Number();
public @Source(FlowPermission.IMEI) String getDeviceId();
}
The above annotates two methods in class TelephonyManager. It indicates that the getLine1Number function returns a String that is a phone number. For more examples, look into the stub files. Also, see the “Annotating Libraries” chapter in the Checker Framework Manual.
When creating a new stub file, see the section “Creating a stub file” in the Checker Framework Manual to learn how to create an initial file and prevent a great deal of repetitive cut-and-paste editing.
It is usually a good idea to annotate an entire API class at a time, rather than to just annotate the specific methods that your app uses. Annotating an entire class lets you think about it once, which takes less time in the long run. It also reduces confusion for people who will later wonder whether a particular method was intended to be unannotated or had not yet been annotated.
Note: at the end of this step, you have not yet added any annotations to the app itself, only to libraries.
Write information flow annotations for your application, in the same way as you did for the libraries. Read the documentation, decide on the types, and write those. A fast and effective way to do this is to grep the source code for words related to information flow properties, such as “camera” or “network”. These words might appear in documentation or in source code. Wherever the words appear, you may be able to write information flow type qualifiers. This approach is both faster and less error-prone than iteratively running the type-checker and fixing the errors that it reports one-by-one.
Focus on the most interesting flow sources and try to connect the flow sources and sinks in the application. Instead of trying to completely annotate only the sources or only the sinks, skim over all the reports and use your intuition to decide which parts of the application to focus on. Try to focus on the parts with the (most) connections between sources and sinks.
Most types will only use either a Source(…)or Sink(…)annotation. The goal is to find places where you need both annotations, e.g. to express that information that comes from the camera may go to the network:
@Source(CAMERA)
@Sink(INTERNET) Picture data;
Such a type connects sources and sinks and one needs to carefully decide whether this is a desired information flow or not.
Once you have written as many type qualifiers as possible, proceed to type-checking (Section 5.3.3).
Run the Flow Checker:
ant check-flow
Eliminate each warning in one of two ways.
An example is a String literal that should be allowed to be sent over the network. By default, every literal has @Sink(CONDITIONAL) and @Source(LITERAL).
@SuppressWarnings("flow") // manually verified to not contain secret data
@Sink(INTERNET) String url = "http://bazinga.com/";
Without warning suppression the assignment raises an error, because string literals have a default annotation of Source(LITERAL). By adding the suppression, you assert that it’s OK to send this string to the network.
After you have corrected some of the errors, re-run ant check-flow. Repeat the process until there are no more errors, or until you find bad code (malicious, or buggy and prone to abuse).
Note: If you want to suppress the NOT_REVIEWED warnings you can run the Flow Checker in the following ways:
ant check-flow-ignorenr
or
ant -Dignorenr=on check-flow
On execution, the Flow Checker creates a file called forbiddenFlows.txt in the current working directory. This file contains a summary of all of the information flows in the app that did not have a flow-policy entry when the Flow Checker was ran. forbiddenFlows.txt is recreated on every execution.
The Flow Checker caches the warning for each use of a forbidden flow. This cache of flow warnings can be filtered, called flow-filtering, using the command:
ant filter-flows -Dfilter="SOURCE -> SINK"
To start tracing information flows, begin by running the Flow Checker:
ant check-flow
Next, inspect the forbiddenFlows.txt file. Concrete flows are flows that do not have {} or CONDITIONAL sinks. Each concrete flow should be evaluated:
After evaluating concrete flows, select a source from the forbiddenFlows.txt to trace. LITERAL sources should be traced last because the unannotated variables have a default source of LITERAL which may be revised. Use flow filtering to display all forbidden flow locations for the selected source.
For example, if forbiddenFlows.txt contains an entry CAMERA→{} this would indicate that a type @Source(CAMERA) flows to a type that had no declared sinks, @Sink({}). CAMERA would be a candidate for tracing. The following command could be used to perform flow-filtering for any flow with a source CAMERA.
ant command filter-flows -Dflow-filter="CAMERA ->"
Flow-filtering displays the source code locations of forbidden flows in the app. Inspect each source location and resolve the forbidden flow by adding annotations or suppressing warnings as described in Section 5.3.3.
Iteratively run the flow-checker, check the forbiddenFlows.txt file, and use flow-filtering to trace forbidden flows throughout the app. Eventually the selected source will flow to one or more concrete sinks. Again, determine if these flow should be added to the flow-policy or marked as malicious.
After adding a flow to the flow-policy and rerunning the Flow Checker, the flow will no longer appear in the forbiddenFlows.txt file. Select another sensitive source file to trace and begin the process again.
Repeat the tracing process until there are no more errors, or until you find bad code (malicious, or buggy and prone to abuse).
Once all warnings were resolved, run
ant -Dsound=true check-flow
Providing the sound option enables additional checks that are required for soundness, but would be disruptive to enable initially. In particular, the tests for casts and array subtyping are stricter. See the discussion in Chapter 3.
This option will also use the stricter conditional rule. (LITERAL → CONDITIONAL rather than the relaxed ANY → CONDITIONAL)
This chapter contains tips for annotating an Android application.
In general, only fields and methods signatures in your own code and in libraries need to be annotated. Usually method bodies do not need to be annotated.
Typically, return types should be annotated with just Source so that the Sink can be inferred from the policy file as explained in Section 3.3.2. Similarly, parameters should only be annotated with Sink, so that the Source can be inferred from the policy file. Local variables should not have to be annotated, because their types can be inferred. Fields must be annotated with Sink or Source, or sometimes both.
The Android API frequently uses callbacks. These are methods that the developer must implement and register. In stub files, these callbacks should be annotated with source information that will be passed when the method is called.
An example annotation of a callback method
package android.hardware;
class Camera$PictureCallback{
//data: a byte array of the picture data
void onPictureTaken
(@Source(CAMERA) byte[] data,
@Source(CAMERA) Camera camera);
}
An example implementation of a callback
public void onPictureTaken
(@Source(CAMERA) byte[] data, @Source(CAMERA) Camera camera){
//If CAMERA->FILE_SYSTEM is in policy file
//Then the following statement will not give an error
writeToFile(data);
}
Some methods take the arguments passed, transform them, and then return them. These sorts of methods should be annotated with @PolySource @PloySink to preserve the flow information. The declaration annotation @PolyFlow can be used instead of annotating all the parameters and return types. See Section 3.6 for more information
Math.min(...) is a good example of these kinds of methods.
package java.lang;
class Math{
@PolyFlow
int min(int i1, int i2);
}
Example use of @PolyFlow.
@Source(LOCATION) int i1 = getLocation();
@Source(INTERNET) int i2 = getLocationForNetwork();
@Source({LOCATION,INTERNET)}) int min = Math.min(i1,i2);
This section explains some common errors issued by the Flow Checker, and gives advice about correcting the errors.
Also see the Checker Framework Manual (http://types.cs.washington.edu/checker-framework/current/checkers-manual.html), which contains information about pluggable type-checking in general. Many of your errors may not be specific to the Flow Checker and are likely to be answered in the Checker Framework Manual.
If you encounter a problem you cannot solve, contact the SPARTA developers (Section 1.2).
Every source-sink pair in your code must be listed in the flow policy or else a forbidden flow error will occur. To correct a forbidden flow error, add the forbidden flow to the policy file.
For example, fix the error below by adding LITERAL -> FILESYSTEM to the policy file.
NewTest.java:43: error: flow forbidden by flow-policy
test = new @Sink(FlowPermission.FILESYSTEM)@Source(FlowPermission.LITERAL) TestClass2(fs);
^
found: @Sink(FlowPermission.FILESYSTEM) @Source(FlowPermission.LITERAL) TestClass2
forbidden flows:
LITERAL -> FILESYSTEM
The most common errors are incompatible types. They can be in arguments, assignment, return, etc.
APIs that have not been annotated have been typed so conservatively that they will always produce incompatible types errors where the required is @Sink(ANY) @Source() or @Sink() @Source(ANY). These errors can be fixed by annotating the API method; Section 5.3.1 explains how to annotate APIs. Below is an example of this sort of error.
HelloWorld.java:84: error: incompatible types in argument
.replace(R.id.container, fragment)
^
found : @Sink(CONDITIONAL) @Source(LITERAL) Fragment
required: @Sink(ANY) @Source({}) Fragment
If the incompatible types error is not from conservative defaulting, then the error must be fixed by adding or removing annotations in the application. For example, the error below can be fixed by adding ACCELEROMETER to the FlowPermission of the return type.
HelloWorld.java:49: error: incompatible types in return.
return x;
^
found : @Sink(CONDITIONAL) @Source({LITERAL, ACCELEROMETER}) int
required: @Sink(CONDITIONAL) @Source(LITERAL) int
As explained in Section 3.1.2, any item in a conditional statement must have CONDITIONAL listed as a FlowPermission. If a variable is only annotated with Source and strict conditionals are not used, then CONDITIONAL is added as a flow sink by default.
For example, if input is a parameter in a method and is annotated with @Sink(FlowPermission.INTERNET), the following error will occur. To fix the error, add CONDITIONAL to the flow sink annotation.
HelloWorld.java:48: error: Conditions are not allowed to depend on flow information.
if(i1 > 2){
^
The goal of an application developer is to create a safe, functional application — and to write the documentation and code so that the safety and functionality are immediately obvious. In particular, the code and documentation should be clear and complete, and the system should pass all the tests that the SPARTA toolset performs. If the application developer fails to meet any of these objectives, then the application will be rejected from the app store, and the fault will be with the application developer, not with the app store.
A malicious developer would need to write clear documentation and code, but would attempt to hide malicious behavior in the app nonetheless. If the documentation or code is not clear, or if the malicious behavior is not well-hidden, or if the SPARTA tools do not confirm that the code conforms to the documentation, then the malicious developer has failed in his task.
Note that the malicious developer’s goal is more difficult than just writing malicious code, and is even more difficult than writing well-hidden malicious code. The reason is that the SPARTA toolset encourages good coding style: poor style requires more warning suppressions. The SPARTA tools lead a programmer to better, clearer code.
Here are some specific requirements of the app developer:
Provide source code. Provide a build file (for Ant, Maven, Android, etc.).
The English description should include how the information flows between parts of the application (the paths along which information flows), and the conditions under which it flows (such as only after a particular user action or external trigger). These will eventually be represented in the SPARTA toolset’s file format and checked by SPARTA, but they are not yet.
If rewriting the code is impossible, then every remaining warning should be suppressed with a @SuppressWarnings annotation. Every @SuppressWarnings annotation requires a clear, compelling justification regarding why the code is actually correct and safe (even though the type-checker cannot prove this property), and why the code cannot be rewritten to address the warning. This justification should be written in the source code at the location of the @SuppressWarnings annotation.
An excessive number of type-checker warnings, or missing justifications for warning suppressions, is grounds for rejection from the app store.
This document contains details that are only relevant to SPARTA developers. Also see the developer-docs directory in the sparta-code repository. Join the SPARTA dev list here: https://mailman.cs.washington.edu/mailman/listinfo/sparta
The SPARTA team uses several Mercurial repositories. Two on DADA:
hg clone https://dada.cs.washington.edu/hgweb/<name>
To access to the DADA repositories you need to be in the sparta web group. (See https://wasp.cs.washington.edu/Internal/hg.html)
And several via SSH
hg clone ssh://buffalo.cs.washington.edu//projects/swlab1/darpa-apac/<name>
To access to the filesystem repositories you need to be in the sparta Unix group. Contact Mike to get the permission.
Also, if you are going to push changes, please add a .hgrc file to your home directory on the server. The .hgrc file should contain:
[trusted] users = wmdietl groups = sparta
This allows emails to be sent when you push changes.
Note that SPARTA as well as the Checker Framework are evolving rapidly. Thus you should periodically get the latest version of the source code (by running hg fetch) and rebuild the projects.
The instructions in this section are only provide as a cheat sheet. Please see the relevant manuals for more information and complete instructions.
Clone the following into a directory called jsr308:
hg clone https://code.google.com/p/jsr308-langtools/ jsr308-langtools hg clone https://code.google.com/p/checker-framework/ checker-framework hg clone https://code.google.com/p/annotation-tools/ annotation-tools hg clone https://plume-bib.googlecode.com/hg/ bib
No password for cloning/pulling, will need google account for pushing.
cd $JSR308/jsr308-langtools/make ant clean clean-and-build-all-tools export PATH=$JSR308/jsr308-langtools/dist/bin:$PATH
cd $JSR308/annotation-tools ant clean ant
cd $JSR308/checker-framework/checkers ant clean ant
To build the Checker Framework without rebuilding the annotated JDKs:
ant bindist-nojdk
http://ant.apache.org/bindownload.cgi
http://developer.android.com/sdk/index.html Install android-15 either in your IDE or from the command line run android
We use LATEXplus Makefiles to create our webpages and manuals. http://latex-project.org/ftp.html You also need HEVEAhttp://hevea.inria.fr/ You may have to copy hevea.sty into sparta-code/docs New to LATEX? http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/LaTeX/Introduction
Install your favorite. Eclipse or VIM/EMACS are the most popular
Help -> Install New Software
Android ADT Plugin: Add new site: https://dl-ssl.google.com/android/eclipse
MercurialEclipse: Add new site: http://cbes.javaforge.com/update
Checker Framework Plugin: http://types.cs.washington.edu/checker-framework/eclipse
You may need to get Android source code to get sense of what API returns (or gets) what type of data. See http://source.android.com/source/index.html You can find the list of all APIs from the Android source code in frameworks/base/api/15.txt - api list for api version 15 (Android 4.0.3) Accessing resource is closely related to Android permissions (some of the resources are not protected with permissions though). The Android permission list is at: http://developer.android.com/reference/android/Manifest.permission.html. Hints to add annotations could be permissionmap (which permission is required to call which functions): http://www.android-permissions.org/permissionmap.html.
Typically for your first commit or for a large change, we review the changes first before you push. After the review, there will likely be several changes you will need to make before you may push your changes.
Before your code is reviewed, the follow should be true:
Once you are ready for a review, send a patch or diff of the changes to be reviewed along with some words describing your changes. To make a patch first hg add all new files then follow the instructions at this link: http://mercurial.selenic.com/wiki/QuickStart#Exporting_a_patch
Eclipse is the dominate IDE in our group. Typically, Eclipse is used to navigate and debug the code but not build the tools. This sections explains how to develop the SPARTA tools using Eclipse.
Join the progress report mailing list, https://mailman.cs.washington.edu/mailman/listinfo/progress-reports. Instructions for writing progress reports can be found here, http://homes.cs.washington.edu/~mernst/advice/progress-report.html.
SPARTA on Jenkins (continuous integration server) http://buffalo.cs.washington.edu:8080/view/SPARTA/
Create a username for Jenkins http://buffalo.cs.washington.edu:8080/securityRealm/addUser
Checker Framework mailing list: https://groups.google.com/forum/?fromgroups#!forum/checker-framework-dev
Android permission maps: